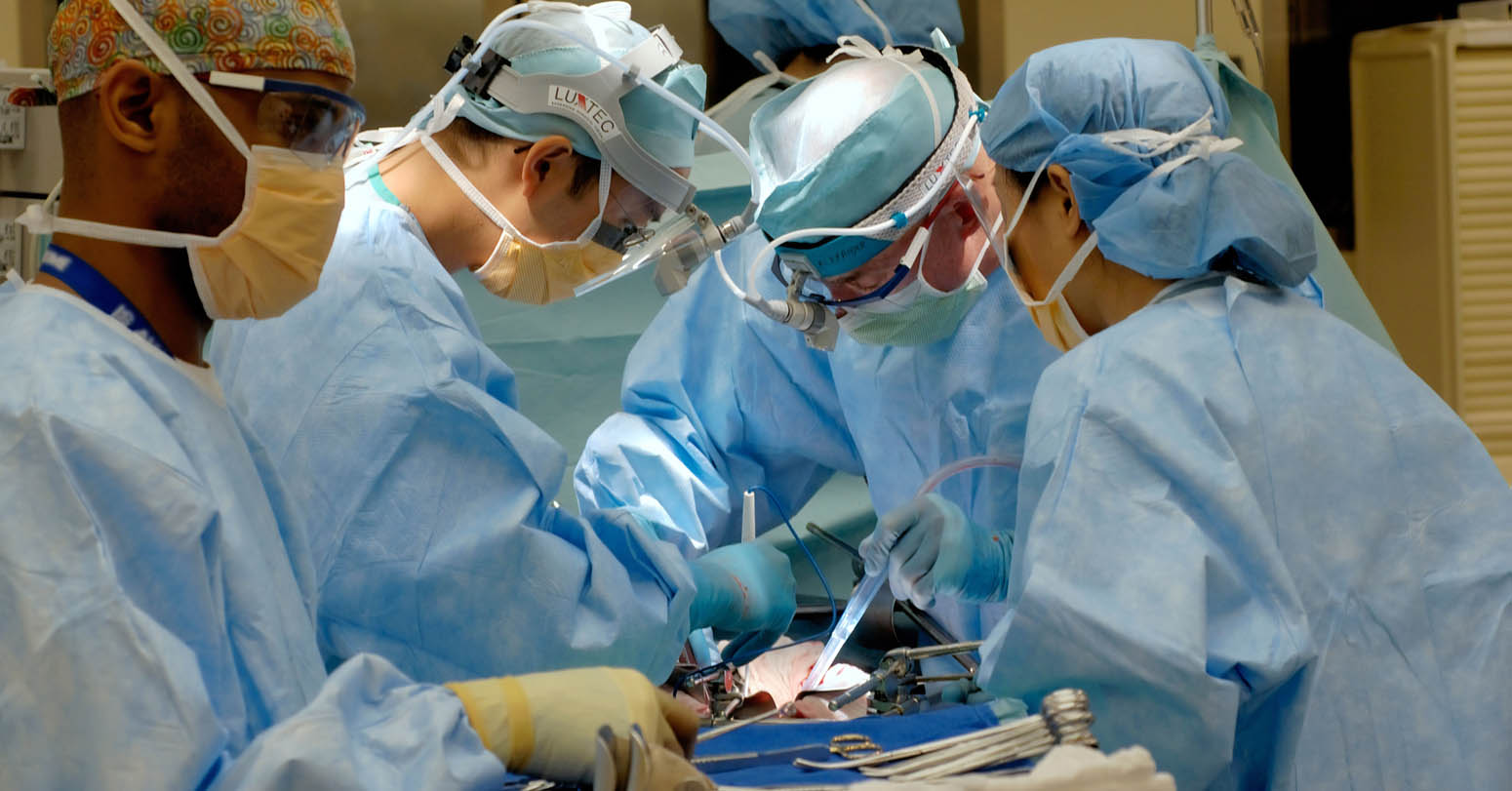
As the lead trauma surgeon at a military hospital in Ukraine’s capital, Petro Nikitin has his hands deep in a war churning hundreds of kilometers (miles) away. The 59-year-old doctor’s work to repair the bodies of some of the most badly injured soldiers is all-consuming.
“I only operate,” Nikitin said, taking a short pause as his team continued surgery on a patient. “I do nothing else in my life now. I don’t see my children, who have been evacuated, I don’t see my wife, who has been evacuated, I live by myself, and all I do is treat the wounded.”
While the Ukrainian military does not provide casualty figures, some Western sources estimate more than 100,000 Ukrainian troops have been killed or wounded since Russia invaded the country almost 15 months ago.
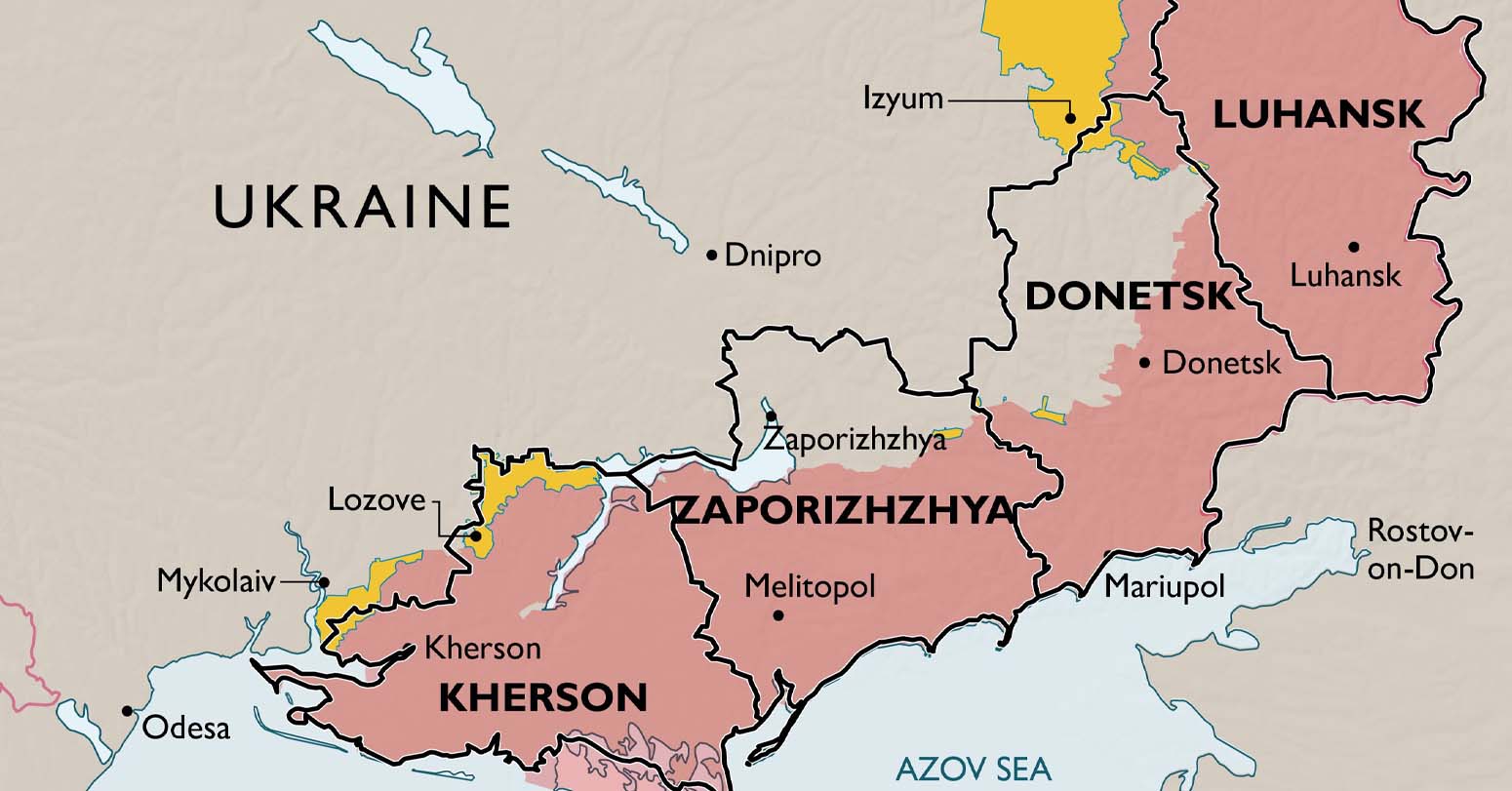
Fighting has been particularly fierce in recent weeks around the eastern city of Bakhmut, scene of the war’s longest and bloodiest battle, where Ukrainian forces have recently clawed back more territory from Russian forces.
A major Ukrainian counteroffensive is expected in coming weeks, with more people likely to end up on operating tables in Nikitin’s hospital, which like other Ukrainian military hospitals, is short-staffed because physicians were pulled away to work in field hospitals closer to the front. The Associated Press agreed not to identify the Kyiv hospital for security reasons.
On Feb. 25, 2022, the day after Russian troops invaded, Nikitin posted a photo on Facebook that showed him listening to an Israeli specialist in treating gunshot wounds. Surgeons from around the world had agreed to participate in an online training on combat-related injuries that Nikitin hastily organized as president of Ukraine’s chapter of an international association of trauma specialists.
“Every one of us had relevant experience before the invasion, but not in such volume,” Nikitin said. “The high numbers of traumas is something new for us.”
Gunshot wounds turned out to be rare. “I don’t even remember the last time I extracted a bullet,” the surgeon said. But during the long days and months, he has become familiar with a range of traumatic injuries: explosive weapons such as landmines, artillery shells and grenades frequently harm many parts of the body at the same time.
“We receive people with damaged legs, chests, stomachs and arms all at once,” Nikitin said. “In such cases, we have to decide what part of the injury should be our priority.”
The military hospital is one of several in Kyiv. As a top-level trauma center, it receives the most complex cases, typically ones involving patients who were stabilized at the front and spent time in a field hospital before their transfer to the capital, Nikitin said.
“We don’t do first aid here. We don’t save lives. That’s done by the medics,” he said. “What we try to do is return these people to a normal life.”
Dealing with wounds involving damage to soft tissue, bone and the structures that bind nerves and veins are the most difficult for his surgical team, Nikitin said. Sometimes they are forced to amputate a soldier’s arm or leg, which “from a moral point of view” is always a gut-wrenching decision, he said.
-AP















Middle-aged man spends millions to
Dr. Dharam Raj Upadhyay: Man
Breathing The Unbreathable Air
Comprehensive Data Protection Law Critically
Gender Differences In Mental Healthcare
Erosion of Democracy